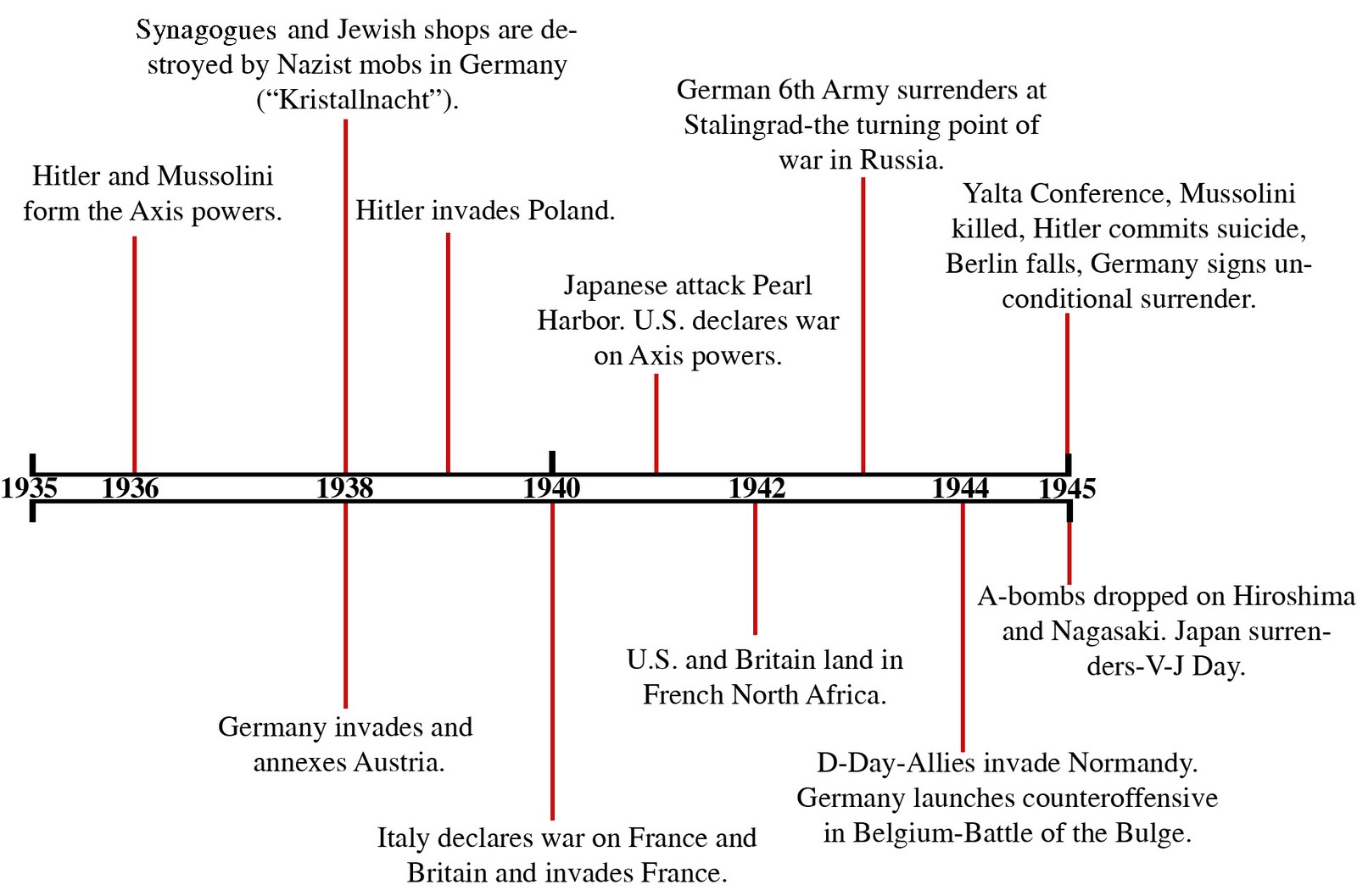
The Second World War, a global conflict that spanned from 1939 to 1945, remains one of the most significant events in human history. The ramifications of this war were felt across continents, altering political landscapes, economies, and societies forever. The timeline of World War II is not just a series of dates; it is a complex narrative of human struggle, bravery, and the quest for power. Understanding this timeline is crucial for comprehending the events that shaped the modern world we live in today.
The WW2 timeline provides a structured overview of key battles, political decisions, and pivotal moments that defined the war. From the initial invasion of Poland to the final surrender of Japan, each event plays a vital role in the broader context of the war. As we delve deeper into the timeline, we uncover the motivations behind decisions made by world leaders and the impact of those decisions on millions of lives.
Moreover, the stories of bravery, sacrifice, and resilience that emerged during this tumultuous period are a testament to the human spirit. By examining the WW2 timeline, we not only honor those who fought and died but also learn valuable lessons about the consequences of conflict and the importance of peace. Let’s embark on this chronological journey through one of history’s most pivotal moments.
What Were the Major Events in the WW2 Timeline?
The WW2 timeline is marked by several major events that shaped the course of the war. Here are some of the most significant milestones:
- September 1, 1939 - Germany invades Poland, marking the start of World War II.
- June 22, 1941 - Operation Barbarossa: Germany invades the Soviet Union.
- December 7, 1941 - Japan attacks Pearl Harbor, leading to the U.S. entering the war.
- June 6, 1944 - D-Day: Allied forces land in Normandy, France.
- May 8, 1945 - V-E Day: Germany surrenders unconditionally.
- August 6 and 9, 1945 - The U.S. drops atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
- September 2, 1945 - Japan formally surrenders, marking the end of World War II.
How Did the War Begin? A Look at the Early WW2 Timeline
The origins of World War II can be traced back to unresolved issues from World War I and the Treaty of Versailles. The interwar period was marked by economic turmoil and the rise of totalitarian regimes, particularly in Germany and Italy. The aggressive expansionist policies of Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini set the stage for conflict. Key events in the early WW2 timeline include:
The Invasion of Poland
On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland, and within weeks, the country was overrun. This invasion was made possible by the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact, which allowed Germany to focus its efforts on Western Europe.
The Fall of France
By May 1940, Germany launched a blitzkrieg against France, leading to its rapid fall. The remarkable speed of the German advance shocked the world and exemplified the effectiveness of their military tactics.
What Were the Turning Points in the WW2 Timeline?
Several key battles and events significantly altered the trajectory of World War II. Understanding these turning points is essential in grasping the overall WW2 timeline. Some of these pivotal moments include:
The Battle of Stalingrad
Between August 1942 and February 1943, the Soviet Union faced a brutal siege at Stalingrad. The defeat of the German army marked a significant turning point in the Eastern Front, as the Soviets began to push back against the Nazis.
The Battle of Midway
In June 1942, the United States achieved a decisive victory at the Battle of Midway, marking a significant shift in naval power in the Pacific Theater. This battle effectively halted Japanese expansion and began a series of offensives by the Allies.
Why Was D-Day So Important in the WW2 Timeline?
D-Day, or the Normandy landings on June 6, 1944, is often regarded as one of the most critical moments in the WW2 timeline. The successful invasion facilitated the liberation of Western Europe from Nazi occupation. The scale of the operation was unprecedented, involving thousands of troops and extensive planning.
The Planning of D-Day
The operation, known as Operation Overlord, required meticulous planning and coordination among Allied forces. The success of D-Day set the stage for the liberation of France and further incursions into German-occupied territory.
The Aftermath of D-Day
Following the success of D-Day, Allied forces continued to advance through France, leading to the eventual liberation of Paris in August 1944. This victory significantly weakened German defenses and boosted Allied morale.
What Led to the End of World War II? A Final Look at the WW2 Timeline
The conclusion of World War II was marked by a series of events that ultimately led to the surrender of the Axis powers. The final months of the war were characterized by intense fighting, strategic bombings, and the introduction of atomic warfare.
The Fall of Berlin
In April 1945, Soviet forces launched a final assault on Berlin, leading to the fall of the city and the suicide of Adolf Hitler on April 30. Germany’s unconditional surrender followed shortly after on May 8, 1945.
The Atomic Bombs and Japan’s Surrender
The United States dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945, leading to Japan's surrender on September 2, 1945. This marked the official end of World War II and ushered in a new era of international relations and nuclear power.
How Did World War II Change the World?
The repercussions of World War II extended far beyond the battlefield. The war led to significant geopolitical changes, including the establishment of the United Nations, the beginning of the Cold War, and a reconfiguration of global power dynamics.
The Formation of the United Nations
In 1945, the United Nations was established to promote international cooperation and prevent future conflicts. This organization aimed to foster peace, security, and human rights on a global scale.
The Cold War Era
The ideological divide between the United States and the Soviet Union following WWII set the stage for the Cold War, a period characterized by political tension and military rivalry that lasted for decades.
Conclusion: Reflecting on the WW2 Timeline
The WW2 timeline encapsulates a complex and multifaceted narrative that continues to resonate in contemporary society. By studying the events of the war, we gain insight into the human experience during times of conflict and the enduring effects of those experiences. As we reflect on this timeline, we honor the sacrifices made by millions and recognize the importance of striving for peace in our world today.
Article Recommendations
- Desmond Howard Net Worth 2023 Updated Figures Amp Insights
- Unique Insights Leo And Ron Gallagher Side By Side
- Fiona Gubelmann Family Life Career And Personal Insights