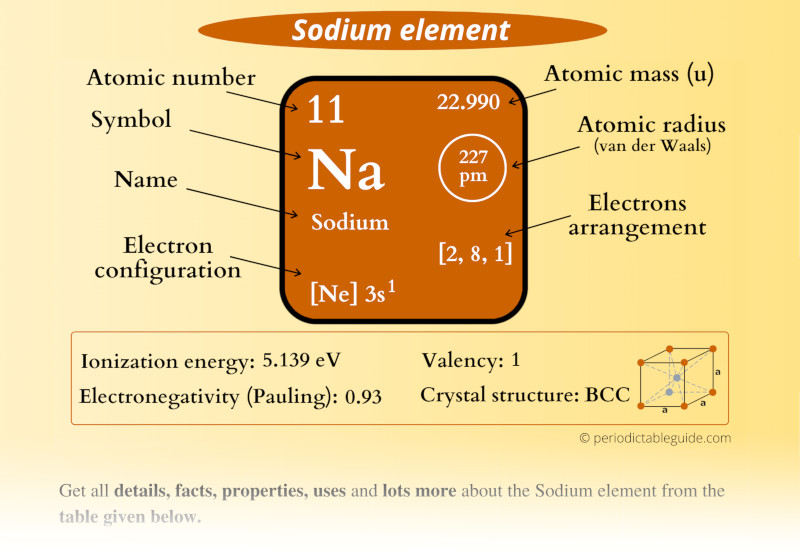
The Na periodic table plays a crucial role in the understanding and organization of elements in the universe. It serves as a comprehensive guide that not only categorizes elements based on their atomic number but also provides insights into their properties, behaviors, and interactions. Sodium, represented by the symbol 'Na', is one of the essential elements included in this table and is fundamental to countless chemical reactions and processes. Understanding the Na periodic table is key to grasping the intricate tapestry of chemistry that governs our world.
With its distinct arrangement and systematic classification, the Na periodic table allows scientists, students, and curious minds to navigate the vast landscape of elements. Each element is organized in a way that highlights its relationships with others, making it easier to predict chemical reactions and discover new compounds. The significance of sodium extends beyond the laboratory; it is vital for numerous biological functions and industrial applications, which makes studying its properties an exciting endeavor.
In this article, we will delve deep into the Na periodic table, exploring the significance of sodium, its applications, and its interactions with other elements. Through a series of engaging questions and comprehensive explanations, we aim to illuminate the importance of this element and how it fits into the broader context of the periodic table. So, let's embark on this intriguing journey to uncover the mysteries of the Na periodic table!
What is the Na Periodic Table?
The Na periodic table refers specifically to the section of the periodic table that includes sodium and its relevant information. Sodium is found in Group 1 of the periodic table, which consists of alkali metals. It has the atomic number 11 and is a highly reactive metal that plays a significant role in various chemical processes.
Why is Sodium Important in Chemistry?
Sodium is critical in chemistry for several reasons:
- It serves as a key component in many chemical reactions, particularly in the formation of compounds.
- Sodium ions are essential for maintaining cellular functions in biological systems.
- It is widely used in the production of sodium compounds, including sodium chloride (table salt), which is ubiquitous in culinary applications.
How Does Sodium React with Other Elements?
Sodium is known for its vigorous reactions, especially when combined with nonmetals. For example:
- When sodium reacts with chlorine, it forms sodium chloride (NaCl), a compound that is essential for human life.
- Reacting sodium with water produces sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas, demonstrating its high reactivity.
What are the Physical Properties of Sodium?
Sodium exhibits several distinctive physical properties:
- It is a soft, silvery-white metal that can be easily cut with a knife.
- Sodium has a low melting point of 97.79 °C (208.0 °F) and a boiling point of 883 °C (1621 °F).
- It is less dense than water, allowing it to float on the surface.
What are the Common Uses of Sodium?
Sodium has a wide array of applications across different fields:
- In the food industry, sodium chloride is crucial for flavoring and preserving food.
- It is used in the manufacturing of soap and glass.
- Sodium vapor lamps, commonly used for street lighting, are another important application.
How Does Sodium Contribute to Biological Systems?
Sodium ions play a vital role in various physiological processes:
- They help regulate fluid balance and blood pressure in the human body.
- Sodium is essential for nerve transmission and muscle contraction.
- It aids in the absorption of nutrients in the intestines.
What are the Safety Considerations When Handling Sodium?
Due to its high reactivity, there are important safety considerations when handling sodium:
- Always store sodium in a dry environment to prevent reactions with moisture.
- Use protective gear, including gloves and goggles, to avoid skin contact and eye exposure.
- Be cautious when working with sodium in laboratory settings, as improper handling can lead to dangerous reactions.
What is the Future of Sodium in Science and Industry?
The future of sodium in science and industry looks promising, especially with ongoing research into its potential applications:
- Advancements in sodium-ion batteries may provide an alternative to lithium-ion technology.
- Sodium-based compounds are being explored for use in pharmaceuticals and agriculture.
Conclusion: Why Should We Study the Na Periodic Table?
Studying the Na periodic table and the element sodium is essential for a deeper understanding of chemistry and its applications in our daily lives. Sodium's unique properties, reactivity, and significance in biological systems make it an invaluable element worth exploring. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or simply a curious individual, delving into the Na periodic table opens up a world of knowledge and discovery that can lead to groundbreaking innovations in science and technology.
| Personal Details | Bio Data |
|---|---|
| Element Name | Sodium |
| Symbol | Na |
| Atomic Number | 11 |
| Group | 1 (Alkali metals) |
| Melting Point | 97.79 °C |
| Boiling Point | 883 °C |
Article Recommendations
- Evaluate Keywords The Ultimate Guide To Maximizing Search Potential
- Cash Money Records Value How Much Are They Worth
- Indepth Profile Of Daci Lynn A Remarkable Talent