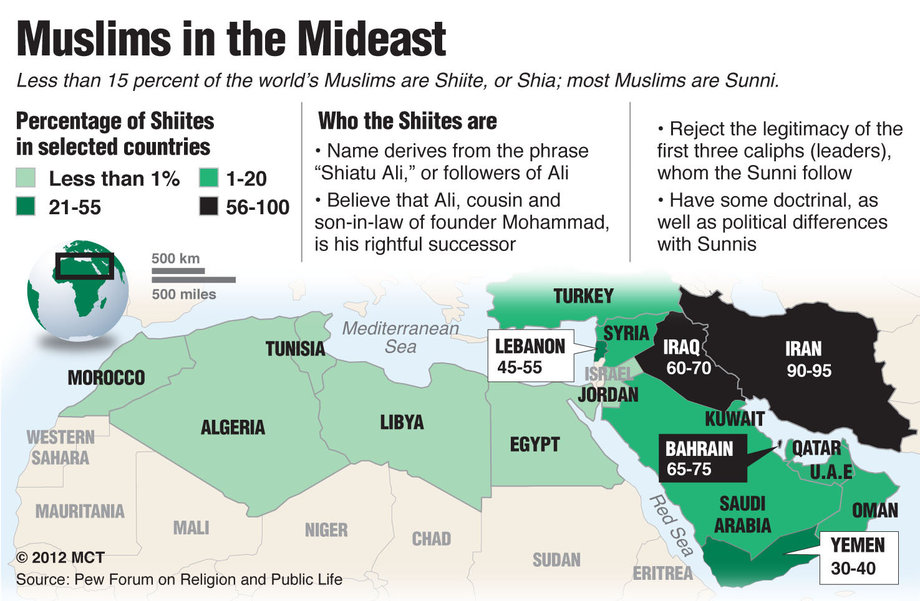
The Islamic faith is one of the world's major religions, with over a billion followers worldwide. Among these believers, two primary sects emerge: Sunni and Shia. While both groups share fundamental beliefs in the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad and the Quran, their historical and theological differences have led to a significant divide that shapes the political and social landscape of many Muslim-majority countries today. The Sunni vs Shia debate is deeply rooted in the early days of Islam, stemming from disputes over leadership succession after the death of the Prophet Muhammad. This article aims to explore the key differences, historical context, and the ongoing implications of this division in contemporary society.
Understanding the Sunni vs Shia divide is crucial for anyone looking to comprehend the complexities of Muslim communities and the conflicts that often arise between them. By delving into the origins, beliefs, and practices of each sect, we can gain better insight into their distinct identities and the factors that contribute to unity and division within the Islamic world. This journey will reveal how theology, history, and culture intertwine to shape the lives of millions.
As we navigate through the intricate tapestry of Sunni and Shia beliefs, we will also address common misconceptions and highlight the shared values that can foster dialogue and understanding. By the end of this exploration, readers will have a clearer view of the Sunni vs Shia landscape and why it matters in today’s global context.
What Are the Historical Roots of Sunni vs Shia?
The Sunni and Shia divide traces its origins back to the early Islamic community following the death of Prophet Muhammad in 632 CE. The crux of the disagreement centered around the rightful successor to the Prophet. Sunni Muslims believe that the community should select its leader, which led to the appointment of Abu Bakr, a close companion of Muhammad, as the first caliph. In contrast, Shia Muslims hold that leadership should remain within the Prophet’s family, specifically in the line of Ali, Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law.
How Did the Split Develop Over Time?
After the initial succession, tensions began to escalate, leading to a series of conflicts and political struggles. Key events, such as the Battle of Karbala in 680 CE, where Husayn, the grandson of the Prophet and son of Ali, was killed, further entrenched the division. This tragic event is particularly significant for Shia Muslims and is commemorated annually during Ashura, a day of mourning.
What Are the Key Beliefs of Sunni Muslims?
- Sunni Muslims make up approximately 85-90% of the global Muslim population.
- They recognize the four main schools of thought in Islamic jurisprudence: Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i, and Hanbali.
- Sunni beliefs emphasize the importance of the community and consensus in decision-making.
- They follow the Sunnah, which includes the teachings and practices of the Prophet Muhammad, as a guide for living a righteous life.
What Are the Key Beliefs of Shia Muslims?
- Shia Muslims constitute around 10-15% of the Muslim population, with significant populations in countries like Iran and Iraq.
- They have their own schools of thought, the most prominent being Twelver Shia Islam, which believes in a line of twelve Imams as spiritual leaders.
- Shia beliefs place a strong emphasis on the role of the Imams as divinely appointed leaders who hold spiritual authority.
- They commemorate the martyrdom of Husayn during Ashura, reflecting their deep connection to the events of Karbala.
What Role Does Politics Play in the Sunni vs Shia Conflict?
The Sunni vs Shia divide is not merely a theological dispute; it has far-reaching political implications. Governments and political movements often exploit these differences to consolidate power or justify conflicts. For instance, the Iranian Revolution in 1979 established a Shia theocracy, heightening tensions with Sunni-majority nations in the region, particularly Saudi Arabia.
How Do Sunni and Shia Muslims Practice Their Faith Differently?
While both sects practice the Five Pillars of Islam—faith, prayer, fasting, almsgiving, and pilgrimage—there are variations in rituals and interpretations. Sunnis typically perform prayers five times a day, while many Shia Muslims combine some prayers, resulting in three distinct sessions. Additionally, Shia Muslims often engage in rituals of mourning, particularly during the month of Muharram.
Can Unity Be Achieved Between Sunni and Shia Muslims?
Efforts toward unity have been made by various leaders and organizations, emphasizing the shared beliefs and values of Islam. Interfaith dialogues and educational initiatives aim to foster understanding and cooperation between Sunni and Shia communities. The challenge remains, however, as historical grievances and ongoing conflicts continue to fuel divisions.
What Is the Future of the Sunni vs Shia Relationship?
The future of the Sunni vs Shia relationship remains uncertain. While there is hope for increased dialogue and collaboration, the political landscape in many regions continues to be influenced by sectarian tensions. As global dynamics shift, it is crucial for both sects to engage in constructive conversations to bridge the gap and work toward a more unified Muslim identity.
Conclusion: Understanding the Sunni vs Shia Divide
In conclusion, the Sunni vs Shia divide is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires nuanced understanding. By examining the historical, theological, and political dimensions, we can appreciate the richness of Islamic belief while acknowledging the challenges that arise from division. Ultimately, fostering dialogue and empathy is essential for building a harmonious future where both Sunni and Shia Muslims can coexist peacefully, united in their faith.
Article Recommendations
- Henry Olyphant Age Quick Facts Info
- How Is Danny Bonaduce Doing Current Health And Career Updates
- Lindsey Graham Defends Mitch Mcconnell Key Details