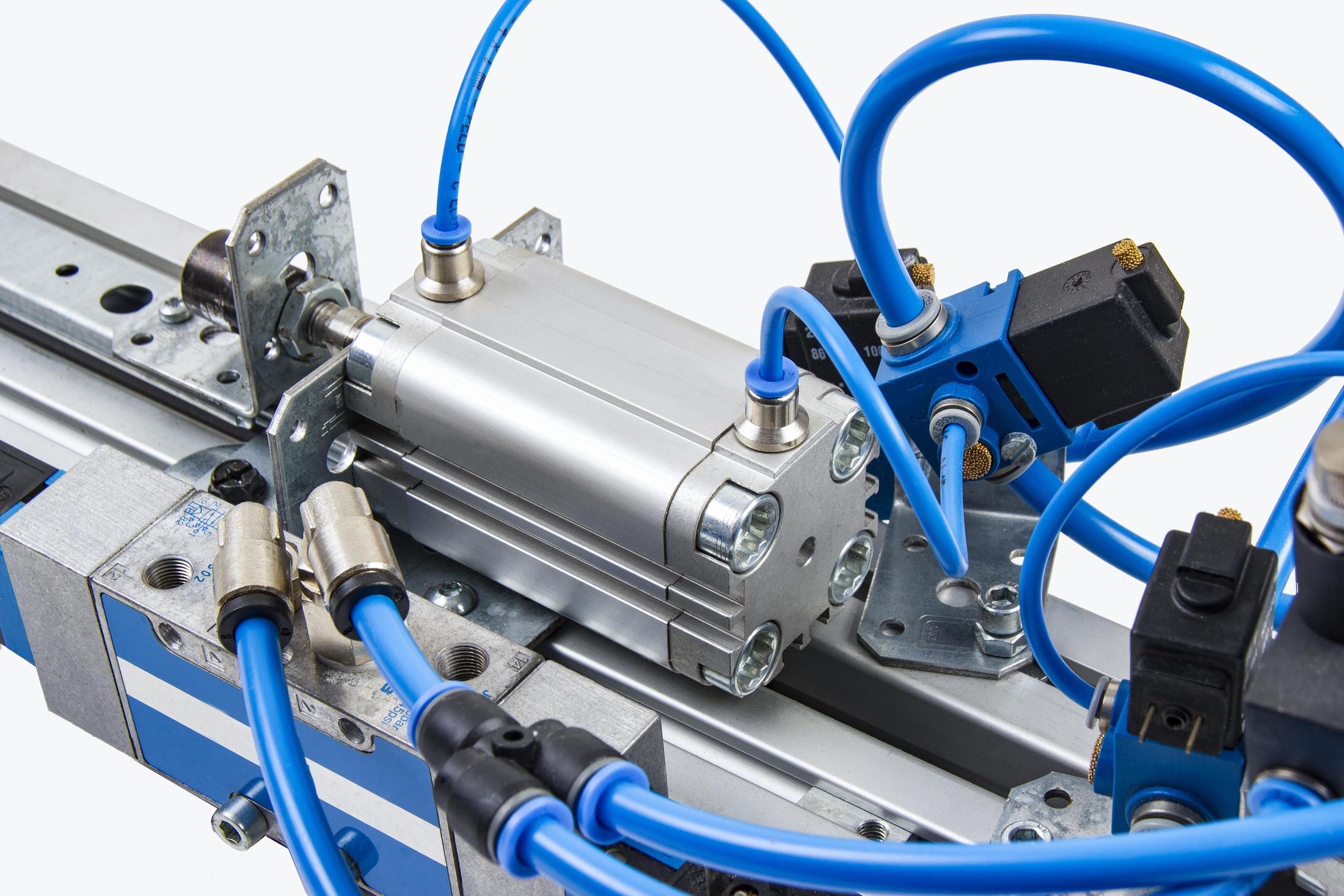
Pneumatics is a fascinating field that revolves around the use of compressed air to generate mechanical motion. It plays a crucial role in various industries, from manufacturing to automotive applications, and has become an integral part of modern technology. The ability to harness the power of air not only makes systems more efficient but also enhances safety and reduces maintenance costs. Understanding the principles of pneumatics can open up a world of possibilities for engineers, technicians, and innovators alike.
In essence, pneumatics encompasses the design, application, and maintenance of equipment that relies on compressed air. By utilizing the properties of air, pneumatic systems can perform a multitude of tasks, including lifting, pushing, and rotating objects. The versatility of pneumatic systems has led to their widespread adoption across various sectors, making them an essential component of modern machinery and equipment.
As we delve deeper into the world of pneumatics, we will explore its fundamental principles, applications, and advantages. This article will also address some common questions that arise regarding pneumatic systems, their efficiency, and future advancements. Whether you're a seasoned professional or a newcomer to the field, understanding pneumatics can significantly enhance your knowledge and skills in technology and engineering.
What Are the Basic Principles of Pneumatics?
Pneumatics operates on several fundamental principles that govern the behavior of gases, particularly air. Here are some core concepts:
- Boyle's Law: This principle states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume at a constant temperature.
- Pascal's Law: This law asserts that when pressure is applied to a confined fluid, the pressure change occurs throughout the fluid equally in all directions.
- Bernoulli's Principle: This principle explains that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in pressure or potential energy.
What Are the Key Components of Pneumatic Systems?
Pneumatic systems consist of several key components that work together to create motion and perform tasks. These components include:
- Compressor: This device compresses air to generate the necessary pressure for the system.
- Storage Tank: A storage tank holds the compressed air until it is needed for operation.
- Valves: Valves control the flow of compressed air into different parts of the system.
- Cylinders: Pneumatic cylinders convert the energy from compressed air into linear motion.
- Actuators: These devices are responsible for converting the pneumatic energy into mechanical work.
What Are the Advantages of Pneumatics?
The utilization of pneumatic systems offers numerous advantages, making them a popular choice in various applications:
- Safety: Pneumatics generally operate at lower pressures compared to hydraulic systems, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Air is abundant and inexpensive, making pneumatic systems financially viable.
- Flexibility: Pneumatic systems can be easily adapted to different tasks and applications.
- Low Maintenance: Pneumatic systems typically require less maintenance than their hydraulic counterparts.
What Are Common Applications of Pneumatics?
Pneumatics is widely used across various industries and applications, including:
- Manufacturing: Pneumatic systems are used in assembly lines for automated material handling and packaging.
- Automotive: Pneumatics is employed in braking systems, air suspension, and robotics for car manufacturing.
- Construction: Pneumatic tools, such as nail guns and jackhammers, rely on compressed air for operation.
- Aerospace: Pneumatic systems are utilized in aircraft for landing gear and door operations.
What Are the Future Trends in Pneumatics?
As technology continues to evolve, so does the field of pneumatics. Some emerging trends include:
- Smart Pneumatics: Integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology for real-time monitoring and control.
- Energy Efficiency: Development of energy-efficient pneumatic systems to reduce operational costs.
- Environmentally Friendly Solutions: Focus on sustainable practices and materials in pneumatic system design.
How Do You Maintain a Pneumatic System?
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of pneumatic systems. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
- Regularly check for leaks in hoses and connections.
- Inspect filters and replace them as needed to ensure clean air supply.
- Lubricate moving parts to reduce wear and tear.
- Monitor system pressure and ensure it remains within operational limits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pneumatics is a dynamic and integral field that harnesses the power of compressed air for various applications. With its advantages, versatility, and potential for future advancements, pneumatics continues to shape the landscape of modern technology. Whether you're involved in engineering, manufacturing, or any other industry, understanding the principles and applications of pneumatics can greatly enhance your expertise and contribute to innovative solutions.
Article Recommendations
- The Truth Behind Megan Fox And Jamie Foxx Are They Related
- D Lucky Slots Real Name Uncover The Truth
- Darius Jackson Net Worth 2023 Estimate Details