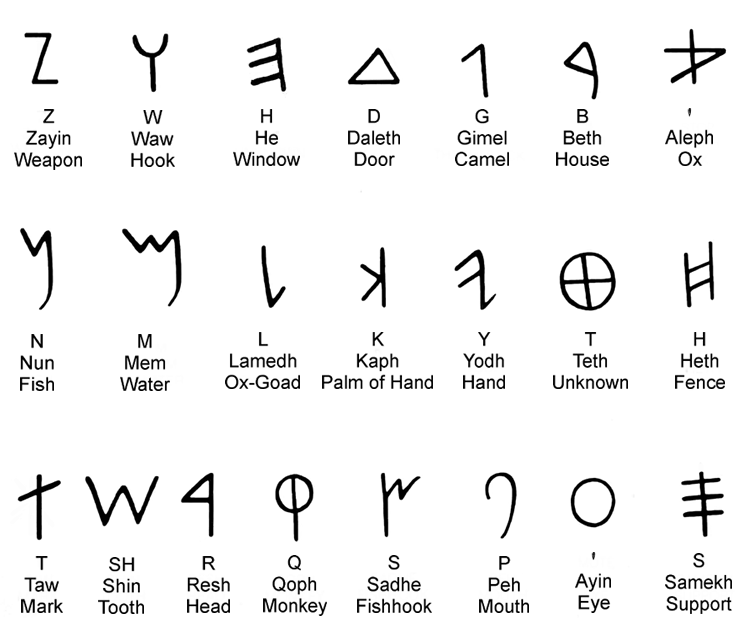
The Phoenician alphabet, a groundbreaking system of writing developed by the ancient Phoenicians around 1200 BCE, holds significant importance in the history of human communication. Serving as the foundation for many modern alphabets, including Greek and Latin, this script reflects the rich maritime culture and trade networks of the Phoenician civilization. As one of the earliest known alphabets, it represents a pivotal shift from pictographic writing systems to an alphabetic one, allowing for greater accessibility and efficiency in written communication.
Understanding the Phoenician alphabet not only sheds light on the linguistic evolution of the time but also illuminates the cultural and historical context in which it thrived. The Phoenicians, known for their seafaring skills and trade expeditions, spread their alphabet across the Mediterranean, influencing various cultures and languages. This article will delve into the origins, characteristics, and lasting impact of the Phoenician alphabet, revealing its vital role in shaping modern communication.
As we explore the intricacies of the Phoenician alphabet, we will address several key questions: How did the Phoenician alphabet come into existence? What makes it unique compared to other writing systems? What is its significance in today's world? By answering these questions, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this remarkable script and its enduring legacy.
What is the Origin of the Phoenician Alphabet?
The Phoenician alphabet emerged around 1200 BCE in the ancient region of Phoenicia, located in present-day Lebanon, Syria, and northern Israel. The Phoenicians, a Semitic-speaking people, initially used cuneiform and hieroglyphic scripts for communication. However, they sought a more efficient system that could easily be adapted for trade and commerce. The result was the creation of a phonetic alphabet comprising 22 consonants, which significantly simplified writing compared to previous systems.
How Did the Phoenician Alphabet Influence Other Writing Systems?
The Phoenician alphabet served as a prototype for several subsequent writing systems, including Greek, Latin, and Arabic. The Greeks adopted and modified the Phoenician script around the 8th century BCE, adding vowels to create a more versatile writing system. This adaptation laid the groundwork for the development of the Latin alphabet, which is used by billions of people today. The influence of the Phoenician alphabet extends beyond the Mediterranean, impacting various scripts across Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa.
What are the Key Characteristics of the Phoenician Alphabet?
The Phoenician alphabet is characterized by its simplicity and efficiency. Here are some key features:
- Composed of 22 consonants, with no vowels.
- Written from right to left.
- Each letter represents a sound, making it phonetic.
- Used primarily for commercial and administrative purposes.
How Did the Phoenician Alphabet Spread Across the Mediterranean?
The Phoenician alphabet's spread can be attributed to the extensive trade networks established by the Phoenicians. As skilled sailors and traders, they ventured to distant lands, establishing colonies and trading posts from North Africa to the islands of the Aegean Sea. This interaction with various cultures facilitated the exchange of ideas, including their writing system. The alphabet's adaptability and ease of use made it appealing to other civilizations, leading to its widespread adoption and modification.
What is the Legacy of the Phoenician Alphabet Today?
The legacy of the Phoenician alphabet is profound, as it laid the foundation for many modern writing systems. Its influence is evident in various languages, showcasing the interconnectedness of human communication. The simplicity and phonetic nature of the Phoenician alphabet paved the way for literacy to become more accessible to the general populace, ultimately shaping the course of history.
What Are Some Notable Examples of the Phoenician Alphabet in Use?
Numerous inscriptions and artifacts featuring the Phoenician alphabet have been discovered, offering insights into its usage. Some notable examples include:
- The Ahiram sarcophagus, which contains one of the oldest known inscriptions.
- Coins minted in ancient Phoenician cities featuring inscriptions in the Phoenician script.
- Various pottery shards and inscriptions found in archaeological sites across the Mediterranean.
How Can We Study the Phoenician Alphabet Today?
Scholars and linguists study the Phoenician alphabet through various methods, including archaeological excavations, historical texts, and comparative linguistics. By analyzing inscriptions and artifacts, researchers gain valuable insights into the phonetic system and its evolution over time. Additionally, modern technology, such as digital imaging and 3D modeling, has enhanced our understanding of ancient scripts, allowing for more accurate interpretations of the Phoenician alphabet.
Conclusion: What Can We Learn from the Phoenician Alphabet?
The Phoenician alphabet serves as a testament to human ingenuity and adaptability in communication. Its development marked a significant transformation in writing, paving the way for literacy and cultural exchange across civilizations. By studying the Phoenician alphabet, we not only gain insights into the past but also appreciate the intricate tapestry of human language and its evolution. The legacy of the Phoenician alphabet continues to resonate in our modern world, reminding us of the enduring power of written communication.
Article Recommendations
- Mcintosh Seahawks Latest News Highlights
- Discover Caseohs Unmasked Whats His True Identity
- Twitchs Net Worth 2024 A Deep Dive